Fish
Fish represent a good source of protein and fat. They offer some distinct
advantages to the survivor or evader. They are usually more abundant than mammal
wildlife, and the ways to get them are silent. To be successful at catching
fish, you must know their habits. For instance, fish tend to feed heavily before
a storm. Fish are not likely to feed after a storm when the water is muddy and
swollen. Light often attracts fish at night. When there is a heavy current, fish
will rest in places where there is an eddy, such as near rocks. Fish will also
gather where there are deep pools, under overhanging brush, and in and around
submerged foliage, logs, or other objects that offer them shelter.
There are no poisonous freshwater fish. However, the catfish species has
sharp, needlelike protrusions on its dorsal fins and barbels. These can inflict
painful puncture wounds that quickly become infected.
Cook all freshwater fish to kill parasites. Also cook saltwater fish caught
within a reef or within the influence of a freshwater source as a precaution.
Any marine life obtained farther out in the sea will not contain parasites
because of the saltwater environment. You can eat these raw.
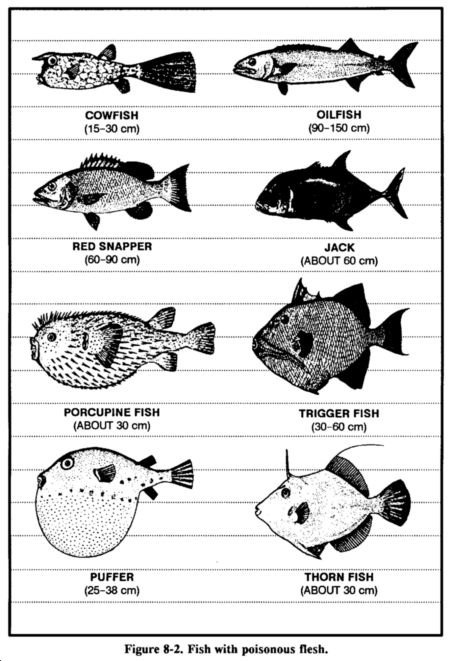
Certain saltwater species of fish have poisonous flesh. In some species the
poison occurs seasonally in others, it is permanent. Examples of poisonous
saltwater fish are the porcupine fish, triggerfish, cowfish, thorn fish,
oilfish, red snapper, jack, and puffer (Figure
8-2). The barracuda, while not actually poisonous itself, may transmit
ciguatera (fish poisoning) if eaten raw.
| Updated:
12 January 2008 |
|
Born on 28 October 1999 |



